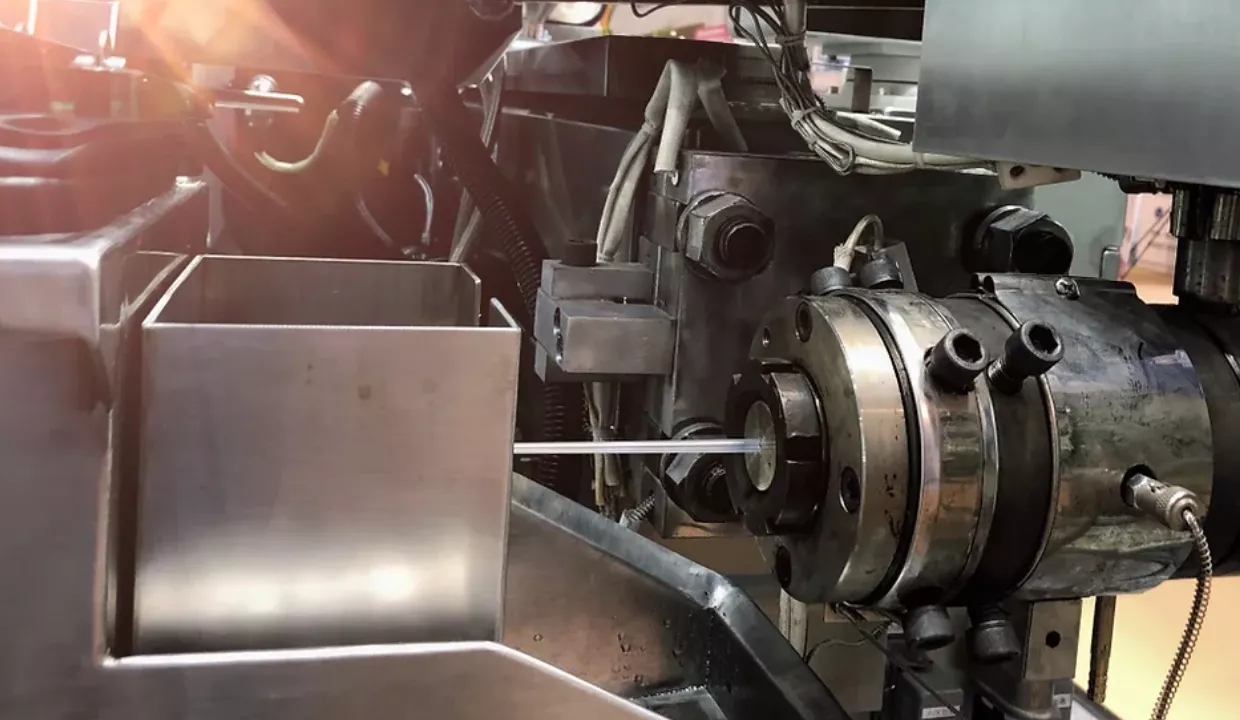
With the advancement of technology, the requirements for injection molding processes are also becoming higher. The choice of injection molding method primarily depends on the type of plastic, its initial form, as well as the shape and dimensions of the product. Common injection molding methods include extrusion, injection molding, blow molding, and calendaring. Each method has its advantages and disadvantages, making it more suitable for specific applications.
Injection Molding
Injection molding works by feeding granular or powdered raw materials into the hopper of an injection machine. The materials are then heated and melted into a flowable state. Under the force of a screw or piston, the molten material enters the mold cavity through the nozzle and the mold’s gating system, where it hardens and takes shape.

Factors affecting injection molding quality: injection pressure, injection time, and injection temperature.
Advantages:
- Short molding cycle, high production efficiency, and easy automation
- Capable of producing plastic parts with complex shapes, precise dimensions, and metal or non-metal inserts
- Stable product quality
- Broad applicability
Applications:
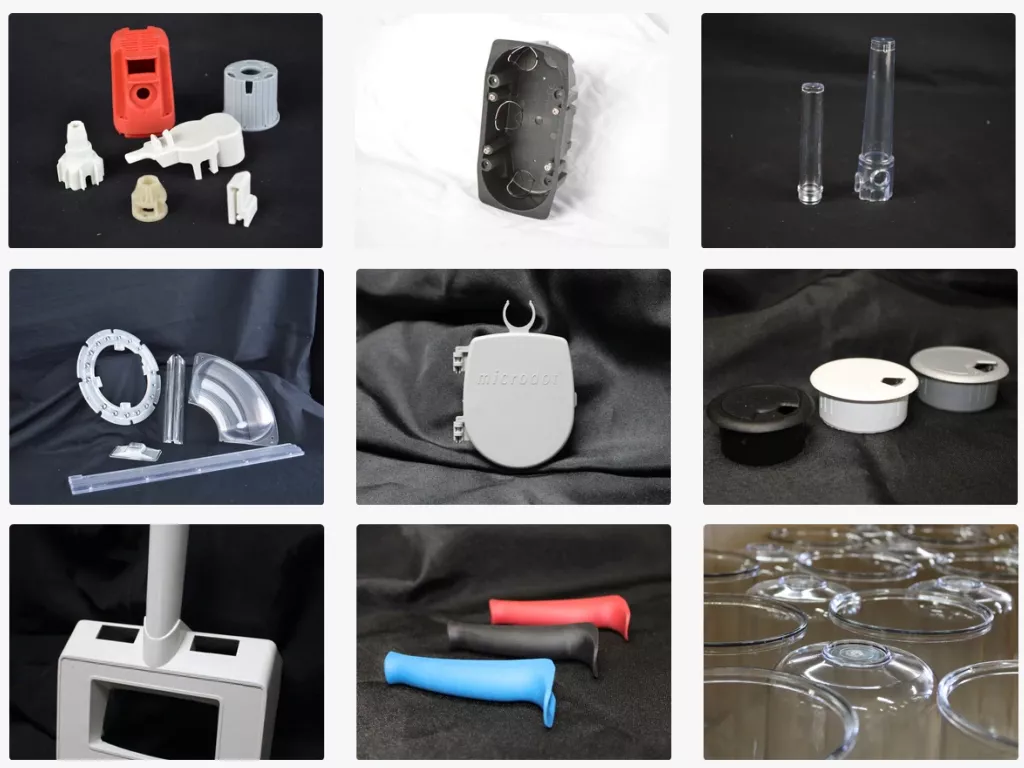

In industrial products, items made by injection molding include kitchenware (trash bins, bowls, buckets, kettles, tableware, and various containers), housings for electrical devices (hair dryers, vacuum cleaners, food blenders, etc.), toys and games, various products in the automotive industry, and parts of many other products.
Learn more about Rilong Injection Molding.
Extrusion Molding
Extrusion molding, also known as Profile Extrusion, is mainly suitable for thermoplastic molding, as well as for some thermosetting and reinforced plastics with good flowability.
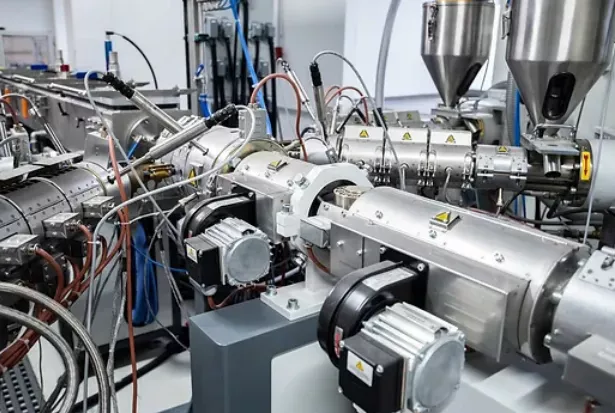

The molding process involves using a rotating screw to push heated, molten thermoplastic material through a die with the desired cross-sectional shape. The material then passes through a shaping device and is cooled and hardened to create a product with the required cross-section.
Process Characteristics:
- Low equipment costs;
- Simple operation, easy control of the process, and well-suited for continuous automated production;
- High production efficiency with uniform, dense product quality;
- By changing the die at the machine head, various cross-sectional shapes of products or semi-finished products can be formed.
Applications:
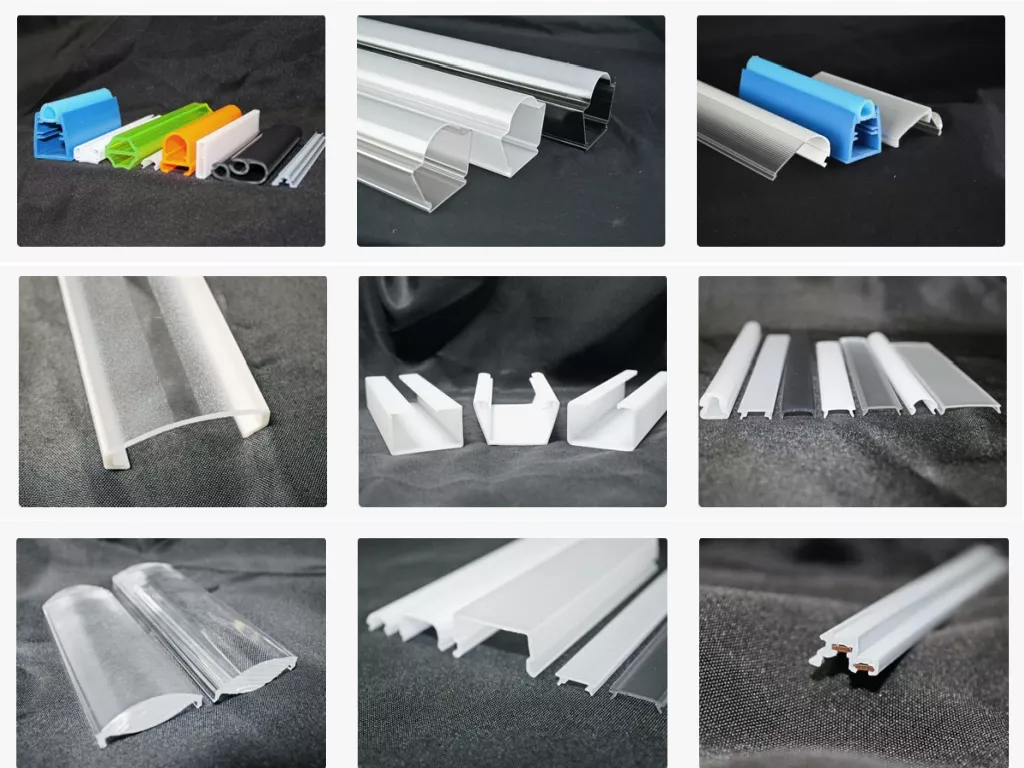

In product design, extrusion molding has wide applicability. Types of extruded products include pipes, films, rods, monofilaments, flat tapes, nets, hollow containers, frames for windows and doors, sheets, cable sheathing, monofilaments, and other special profiles.
Calendering
Calendering is a process in which plastic raw materials are passed through a series of heated rollers, where they are compressed and stretched to form films or sheets.

Process Characteristics:
Advantages: High product quality, large production capacity, and suitability for continuous automated production.
Disadvantages: Large equipment size, high precision requirements, numerous auxiliary equipment, and product width are limited by the roller length of the calendar.
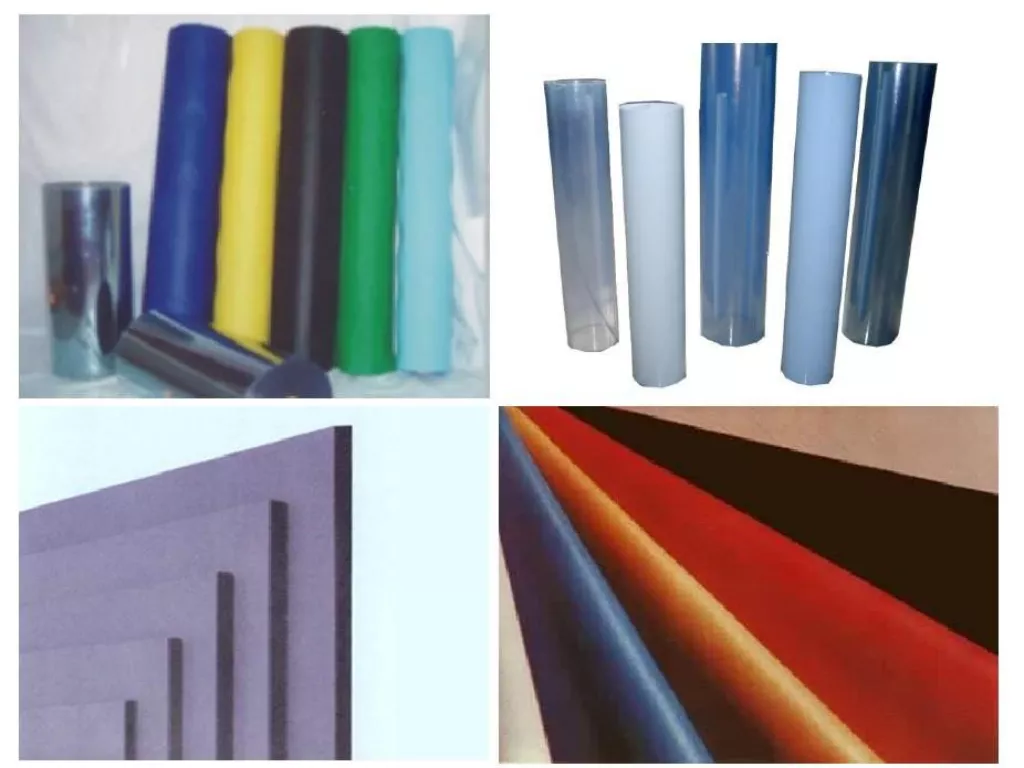
Applications:
Commonly used for producing soft PVC films, sheets, artificial leather, wallpaper, and floor coverings.
Blow Molding
Blow molding is a process where processed raw materials are placed in a split mold, and compressed air is introduced to press the preform against the inner mold walls. After cooling, the molded part is ejected. Blow molding is generally divided into film blow molding and hollow blow molding.
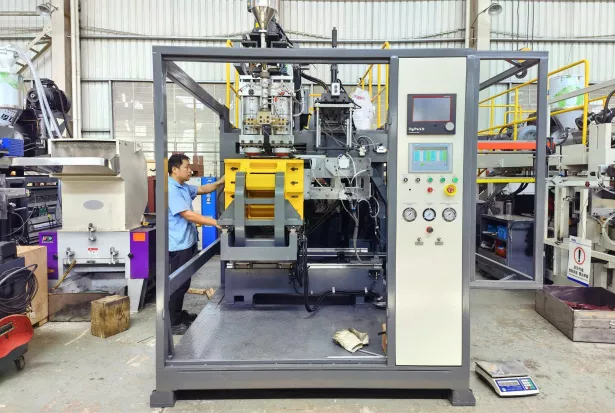

- Film Blow MoldingFilm blow molding extrudes molten plastic from the annular gap of the die head into a cylindrical thin-walled tube. Compressed air is then introduced into the tube through the die’s center hole, expanding it into a larger-diameter tubular film (commonly called a bubble tube). After cooling, the film is wound.
- Hollow Blow MoldingHollow blow molding uses air pressure to inflate a rubber-like process within a mold cavity, producing hollow products. It is a secondary molding technique for making hollow plastic items. Based on the preform production method, hollow blow molding can be classified into extrusion blow molding, injection blow molding, and stretch blow molding.
Advantages:
Products have uniform wall thickness, minimal weight tolerance, require less post-processing, generate minimal scrap, and have lower production costs. They offer high resistance to tensile, impact, bending, and environmental stresses, making them suitable for producing high-volume, small-precision items.
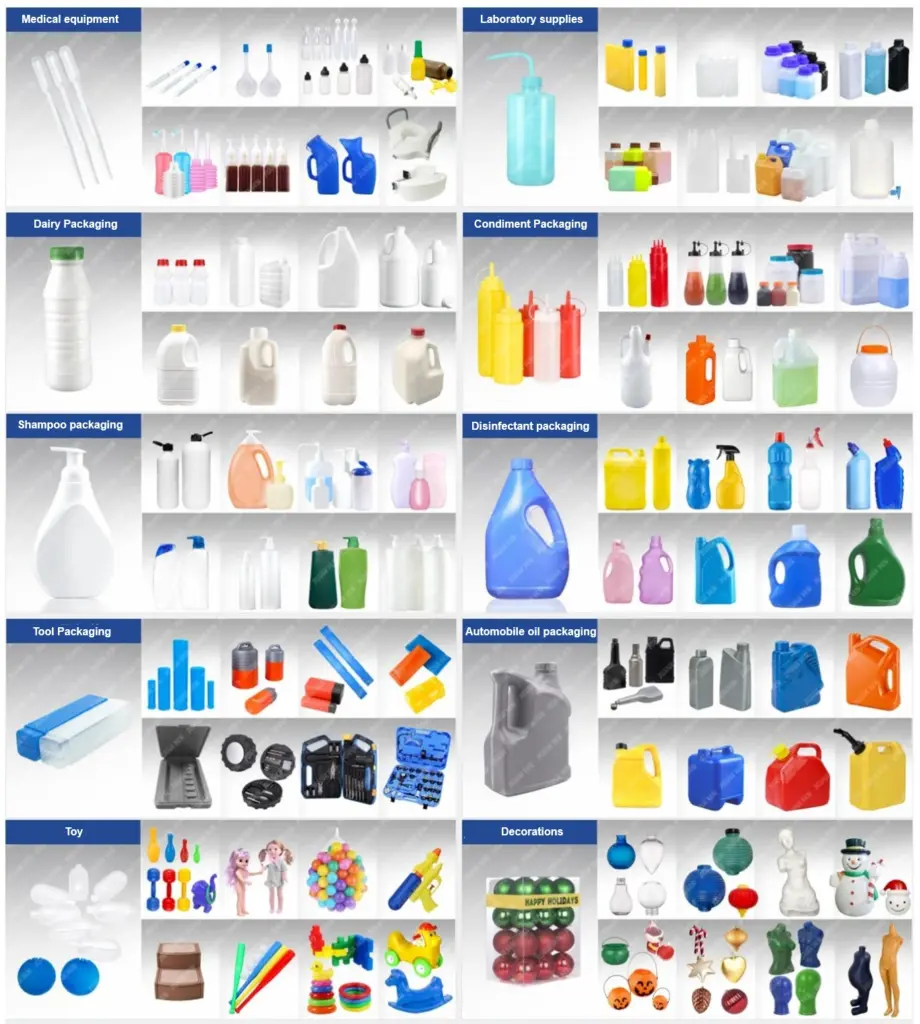

Applications:
Hollow blow molding is used to create hollow plastic products, such as bottles, packaging containers, spray bottles, fuel tanks, cans, and toys.
Film blow molding is primarily used for manufacturing plastic films.
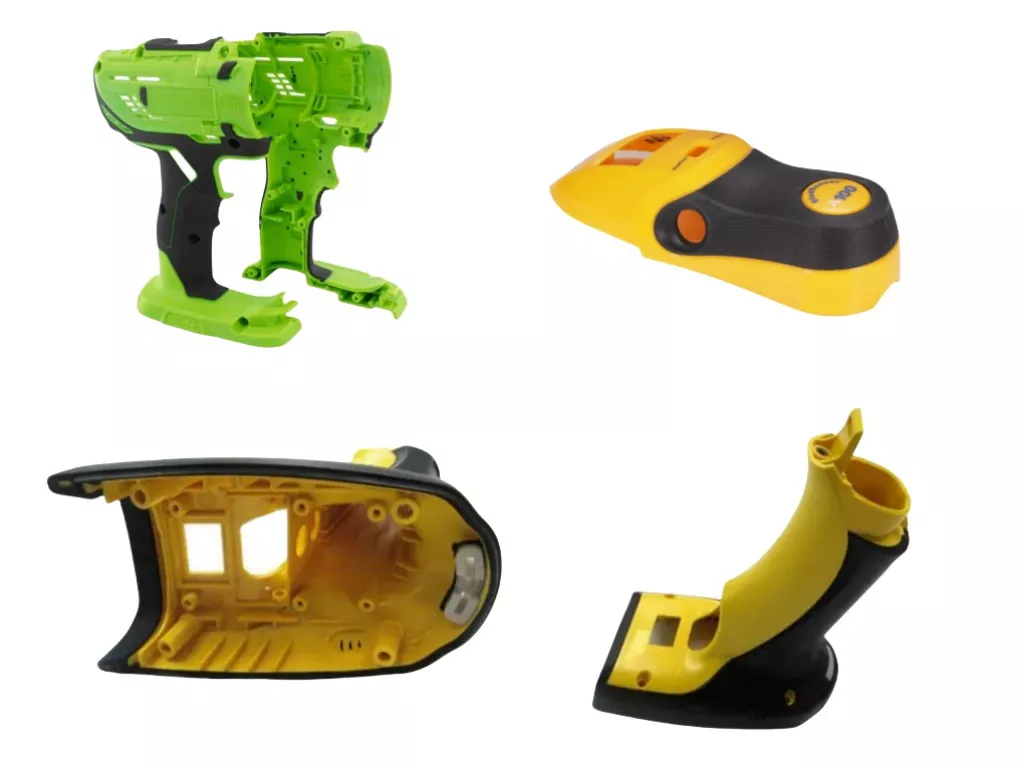
Two-Color Injection Molding
Two-color injection molding is a method of injecting two different-colored plastics into the same mold. This process allows the plastic part to display two distinct colors and can create either patterned or irregular cloud-like designs, enhancing both functionality and aesthetics.

Process Characteristics:
Proper combinations of skin and core materials can reduce residual stress, increase mechanical strength, or improve the surface properties of the product.
The core material can use low-viscosity materials to reduce injection pressure.
Core material can be recycled for reuse.
Depending on the product’s requirements, such as a thick product, a soft outer layer can be used, with a hardcore material, or a foamed plastic core can be used to reduce weight.

Lower-quality core materials can be used to reduce costs.
Expensive skin or core materials with unique surface properties can be used to enhance product performance.
Nano Molding Technology (NMT)
NMT (Nano Molding Technology) is a technique that combines metal and plastic using nanotechnology. First, the metal surface undergoes a nanometer-level treatment, allowing the plastic to be directly molded onto the metal surface, forming an integrated metal-plastic part.
Nano Molding Technology includes two process types based on the plastic’s placement: one where the plastic is non-visible, forming a fully integrated structure, and the other where the plastic is a visible part of the finished surface.
Process Characteristics:
- Provides a metallic appearance and texture,
- Simplifies component design, making products lighter, thinner, shorter, and more compact,
- Reduces production costs while achieving high bonding strength and significantly lowering the use of related materials.

Applications:
NMT is commonly used in electronic products, such as mobile phone casings and laptop housings.