Meet Rilong Precision Mold at Embedded World 2026, Stand 3A-366.

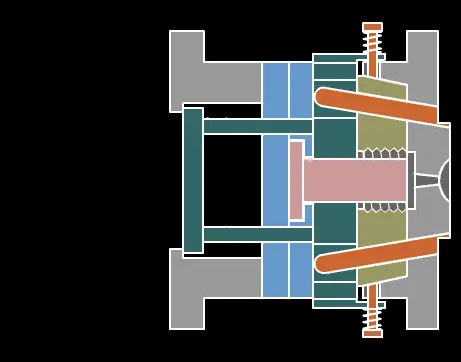
Injection molding is a method for shaping industrial products during manufacturing. Common materials include rubber and plastic. It can be further categorized into injection compression molding and die-casting methods. The injection molding machine is the primary equipment used to produce various plastic products by shaping thermoplastics or thermosetting materials with plastic molds. Injection molding is accomplished through the combined use of injection machines and molds.
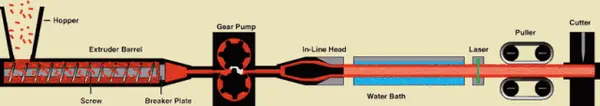
In extrusion, material is heated and plasticized as it moves through the barrel and screw of an extruder, while simultaneously being pushed forward by the screw. It then passes continuously through the die to form products or semi-products with specific cross-sections.
Also known as roto-molding, rotational molding, or rotational casting, this method involves placing a measured amount of plastic (in liquid or powder form) into a mold. Once the mold is closed, it rotates around two perpendicular axes while being heated. The material gradually melts and adheres uniformly to the mold cavity’s surface, taking its shape. After cooling and solidification, the product is de-molded.
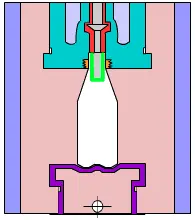
Blow molding, also called hollow blow molding, is a rapidly developing plastic processing method. A thermoplastic resin tube, formed by extrusion or injection molding, is placed into a split mold while still hot (or reheated to a softened state). After the mold is closed, compressed air is introduced into the tube to inflate it against the mold walls. Once cooled and de-molded, a hollow product is formed.
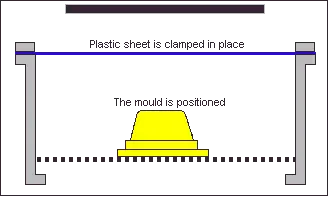
Vacuum forming is a plastic processing technique in which a flat plastic sheet is heated until softened and then vacuum-sucked onto a mold’s surface. After cooling, the product is shaped. This technique is widely used across various industries.

Also called press molding, this process involves placing powder, granules, or fiber-based plastics into a heated mold cavity. The mold is closed and subjected to pressure, forming and curing the material. This technique works with thermosetting plastics, thermoplastics, and rubber materials.
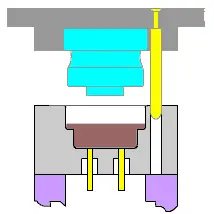
In calendering, molten thermoplastic material is passed through gaps between two or more parallel, counter-rotating rolls. The molten material is compressed, stretched, and flattened into sheets of specific dimensions and quality. This method is often used for producing plastic films or sheets.
Foaming involves adding a foaming agent to materials like PVC, PE, and PS to create a microcellular structure. Both thermosetting and thermoplastic plastics can be converted into foam plastics, making this a significant area in plastic processing.
This process involves wrapping resin-soaked continuous fibers (or fabric strips, prepreg yarns) around a mandrel in a specific pattern. After curing and demolding, the desired product is obtained.
Lamination is a process where multiple layers of the same or different materials are bonded under heat and pressure to form a single structure. This method is used in plastic and rubber processing.

Coating involves applying plastic sol or organic solutions to surfaces such as fabric or paper, producing items like artificial leather, oilcloth, or plastic wallpaper. Powdered plastics can also be applied to metal surfaces. Examples of plastic-coated products include artificial leather, plastic wallpaper, and coated metal items.
Casting is an early plastic processing method where liquid monomers or pre-polymers are poured into a mold and polymerized into a solid product. Modern casting techniques now use polymer solutions, dispersions, or melts, expanding their applications.
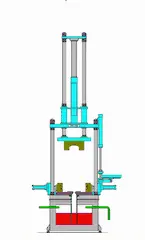
This technique uses thermoplastic materials, which flow in certain conditions and solidify at room temperature. Using specific tools, the material is shaped in its molten state and then cured at room temperature to form the desired product.
A type of compression molding is conducted at room temperature. The molded product can then be further heated or cured chemically to achieve the desired properties.
Primarily used for thermosetting plastics, this method involves heating the material until it melts, applying pressure to mold it, and further heating to crosslink and cure.
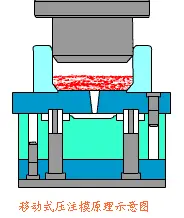
This process injects resin into a closed mold to impregnate reinforcement materials and then cures the resin. RTM eliminates the need for pre-impregnated materials or autoclaves, reducing equipment and production costs. It is widely used in the aerospace, automotive, and shipbuilding industries.
This pressure processing method involves pressing a billet in a mold cavity using a punch or die, causing the material to flow plastically and form a shape corresponding to the mold.
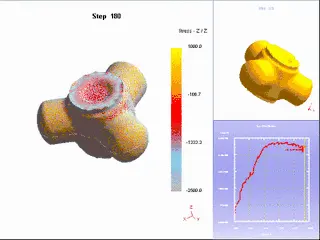
Thermoforming is a specialized method of processing thermoplastic sheets. Sheets are heated to a softened state, clamped, and shaped by applying force to conform to a mold surface. After cooling, the formed part is trimmed into a finished product.
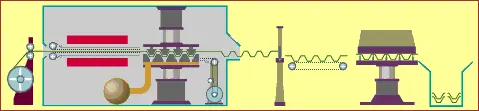
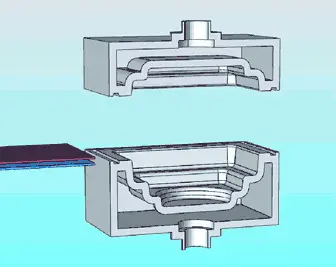
A form of rapid prototyping, 3D printing constructs objects layer by layer using digital files and materials like powdered metals or plastics. It is widely used in mold manufacturing and industrial design and is increasingly applied to produce finished components. Common 3D printing materials include nylon, PLA, ABS resin, durable nylon, gypsum, aluminum, titanium alloy, stainless steel, and rubber.

Learn more about Rilong Plastic Injection Molding.