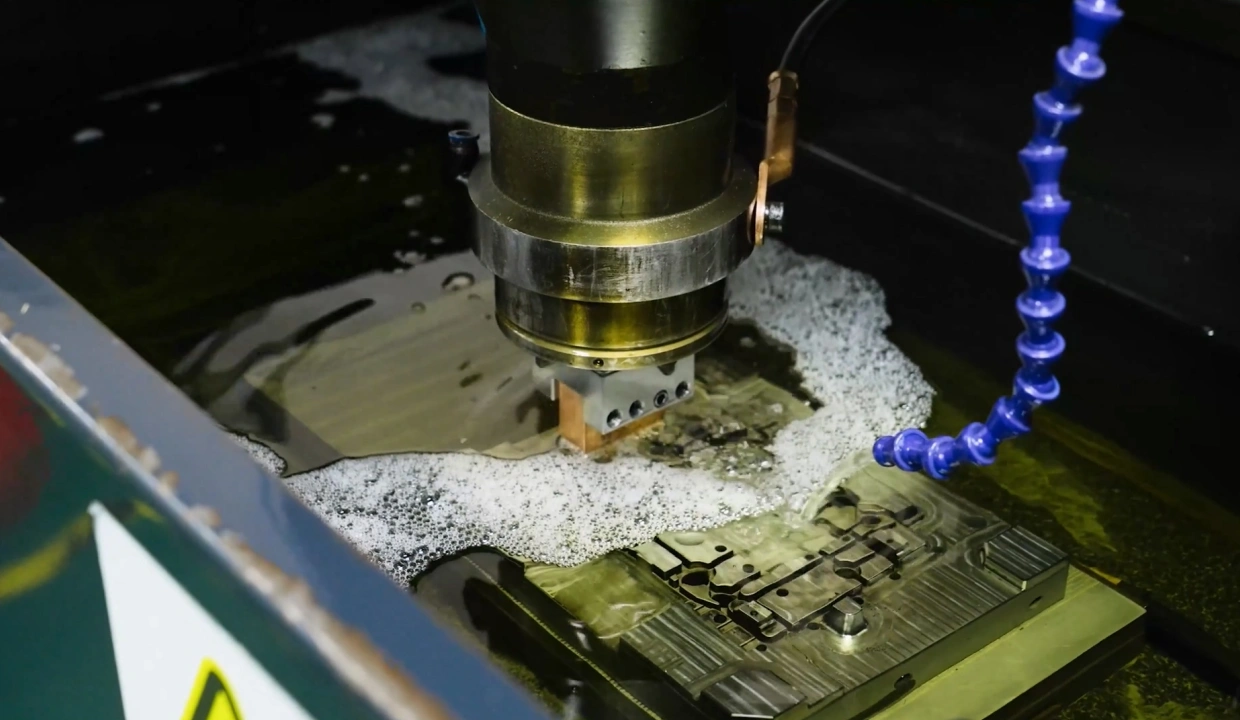
Mold customization is a crucial process in the manufacturing industry, allowing for the creation of unique and precise parts but also presents several challenges. This article explores both aspects to provide a comprehensive understanding of the topic.
Here are the key steps involved in mold customization:
1. Design Conceptualization
The first step in mold customization involves:
- Understanding the client’s requirements
- Creating initial sketches and 3D models
- Considering factors like material, part geometry, and production volume
2. Computer-Aided Design
This step includes:
- Developing detailed 3D models of the part and mold
- Simulating mold filling and cooling processes
- Optimizing design for manufacturability
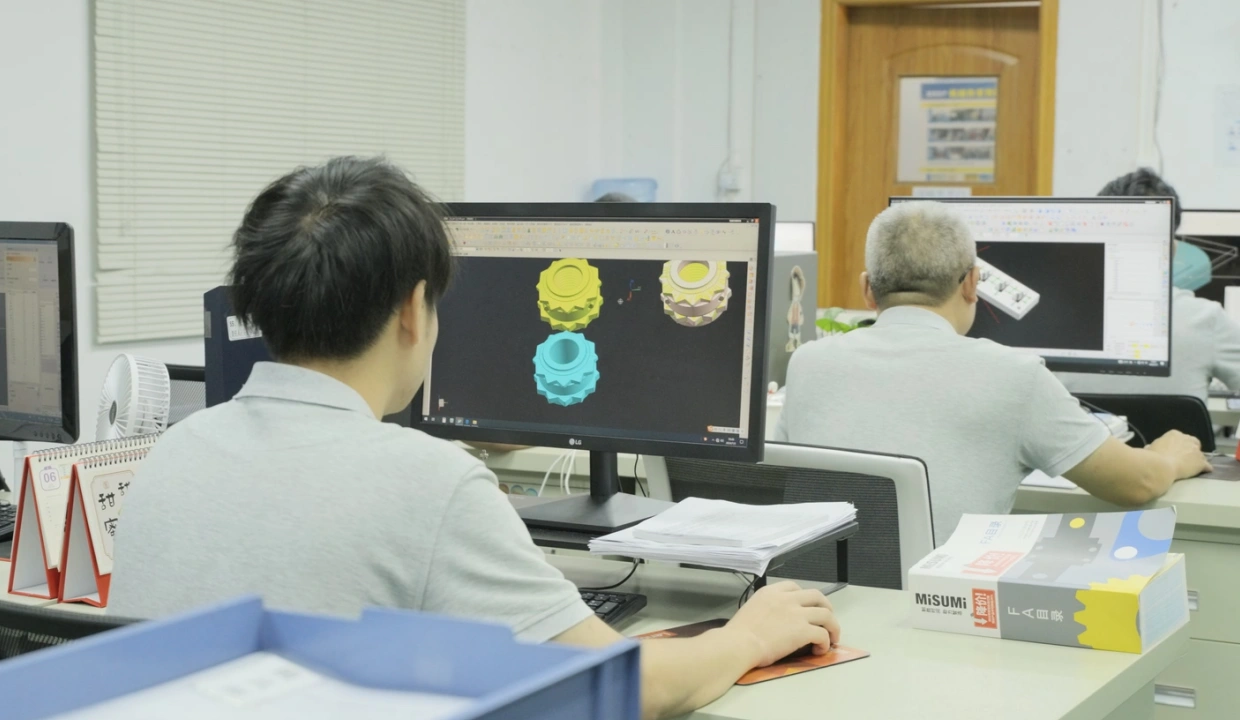

3. Material Selection
Choosing the right materials for both the mold and the final product, considering:
- Durability requirements
- Heat resistance
- Cost-effectiveness
4. Prototyping
Before full-scale production, prototyping involves:
- Creating a sample mold or part using 3D printing or CNC machining
- Testing the prototype for fit, form, and function
- Making necessary adjustments based on prototype performance
5. Mold Manufacturing
The actual creation of the mold, which may include:
- CNC machining of mold components
- EDM (Electrical Discharge Machining) for intricate details
- Surface treatments and coatings for improved performance
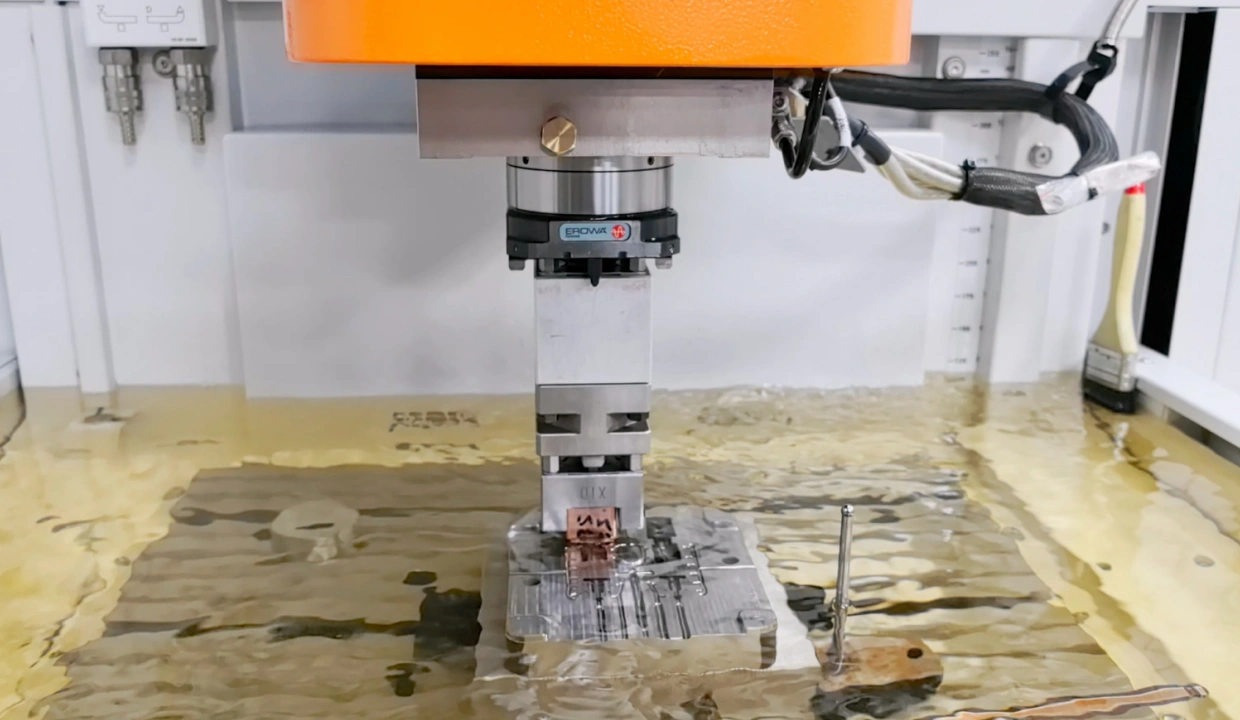

6. Quality Control and Testing
Ensuring the mold meets all specifications through:
- Dimensional checks
- Surface finish inspections
- Trial runs to test mold performance
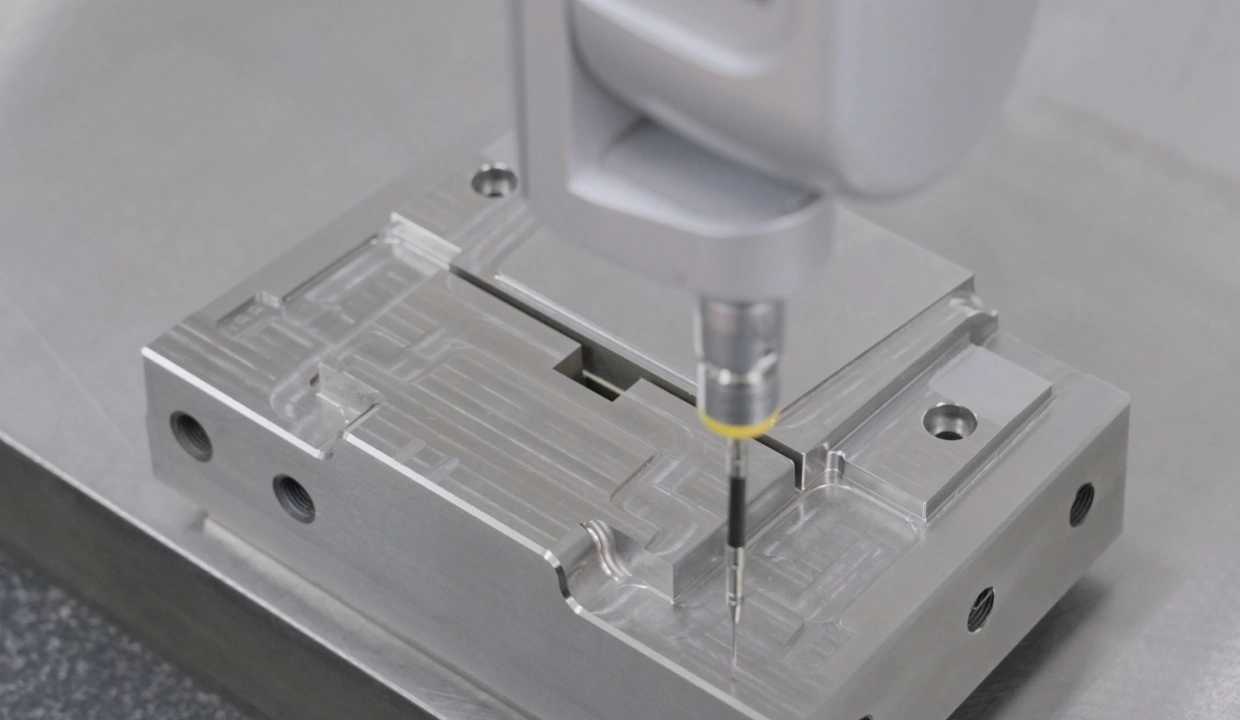

7. Refinement and Optimization
Based on initial testing, this step may involve:
- Fine-tuning mold design
- Adjusting cooling systems
- Optimizing cycle times
8. Final Approval and Production
The final steps include:
- Client approval of sample parts
- Setting up for full-scale production
- Implementing quality control measures for ongoing manufacturing
By following these steps, manufacturers can create customized molds that meet specific product requirements, ensuring high-quality, efficient production of unique parts.
Challenges of Mold Customization
1. Higher Initial Costs
Custom molds typically involve:
- Significant upfront investment in design and manufacturing
- Longer development times
- Potentially higher material costs for specialized mold construction
2. Complexity in Design and Manufacturing
Creating custom molds requires:
- Specialized expertise in mold design and engineering
- Advanced software and technology for design and simulation
- Skilled technicians for manufacturing and maintenance
3. Longer Lead Times
The customization process often results in:
- Extended design and approval phases
- Longer manufacturing times for the mold
- Potential delays in product launch
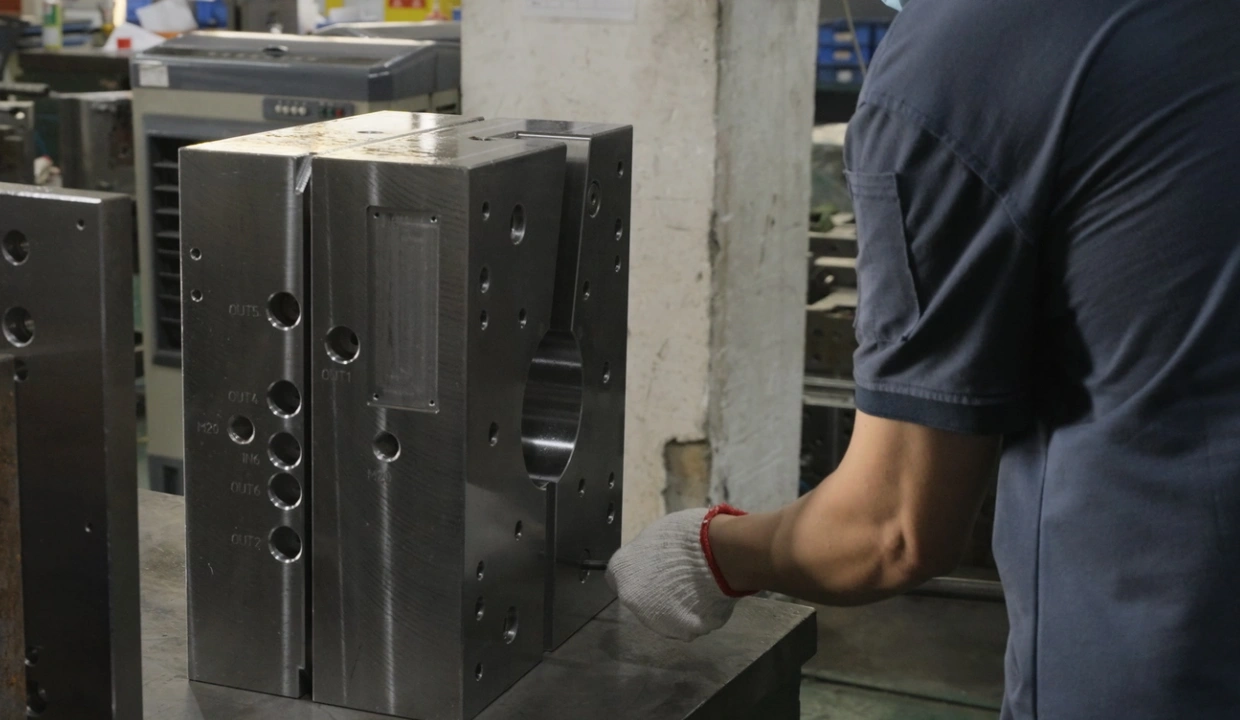
4. Maintenance and Repair Challenges
Custom molds may present difficulties in:
- Finding replacement parts
- Requiring specialized knowledge for repairs
- Potentially longer downtime during maintenance
5. Risk of Obsolescence
Highly customized molds face the risk of:
- Becoming obsolete if product designs change
- Limited flexibility for future modifications
- Potential for unused inventory if product demand shifts

Conclusion
Mold customization offers significant benefits in terms of product quality, production efficiency, and market competitiveness. However, it also presents challenges related to costs, complexity, and long-term flexibility. Manufacturers must carefully weigh these factors when deciding whether to invest in custom molds, considering their specific production needs, market demands, and long-term business strategies.



