In modern manufacturing, ensuring a secure and reliable connection between plastic and metal components is a key challenge across industries such as automotive, electronics, and home appliances. Achieving durable, high-strength joints directly impacts product performance, safety, and lifecycle.
Heat staking and heat riveting are two proven and widely used joining methods that utilize the thermal properties of plastics to create strong mechanical bonds—without the need for adhesives or additional fasteners. This article explores how these processes work, their benefits, and how to choose the right solution for your application.
What Is Heat Staking?
Heat staking is the process of embedding a metal insert (typically brass) into a molded plastic hole using heat and pressure. The plastic softens and flows around the knurled or threaded surface of the insert, forming a strong mechanical bond once cooled.
Typical Process Steps:
- Designing the Hole: The hole in the plastic is slightly smaller than the insert for a tight interference fit.
- Insert Positioning: The insert is manually or automatically placed into the hole.
- Heating and Pressing: A heated tool presses the insert into the plastic, softening it.
- Cooling and Solidifying: Pressure is maintained while the plastic cools, locking the insert in place.
Advantages of Heat Staking:
- Enables repeatable assembly and disassembly
- Provides strong, wear-resistant threads in plastic parts
- Compact and clean appearance with inserts embedded inside
- Ideal for high-volume, automated production
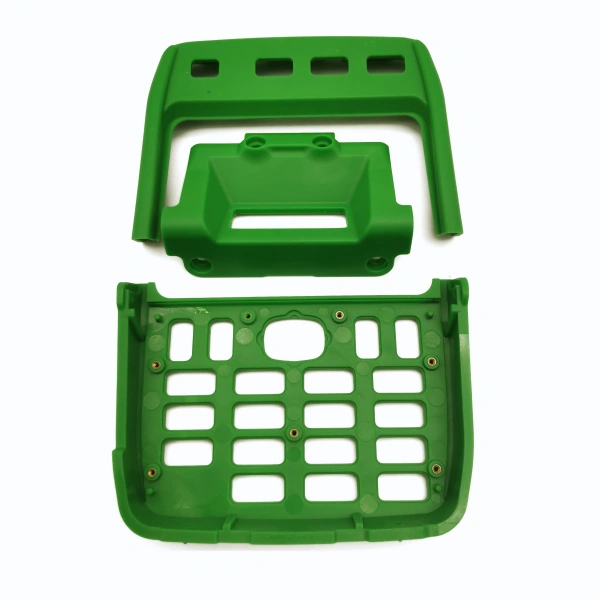
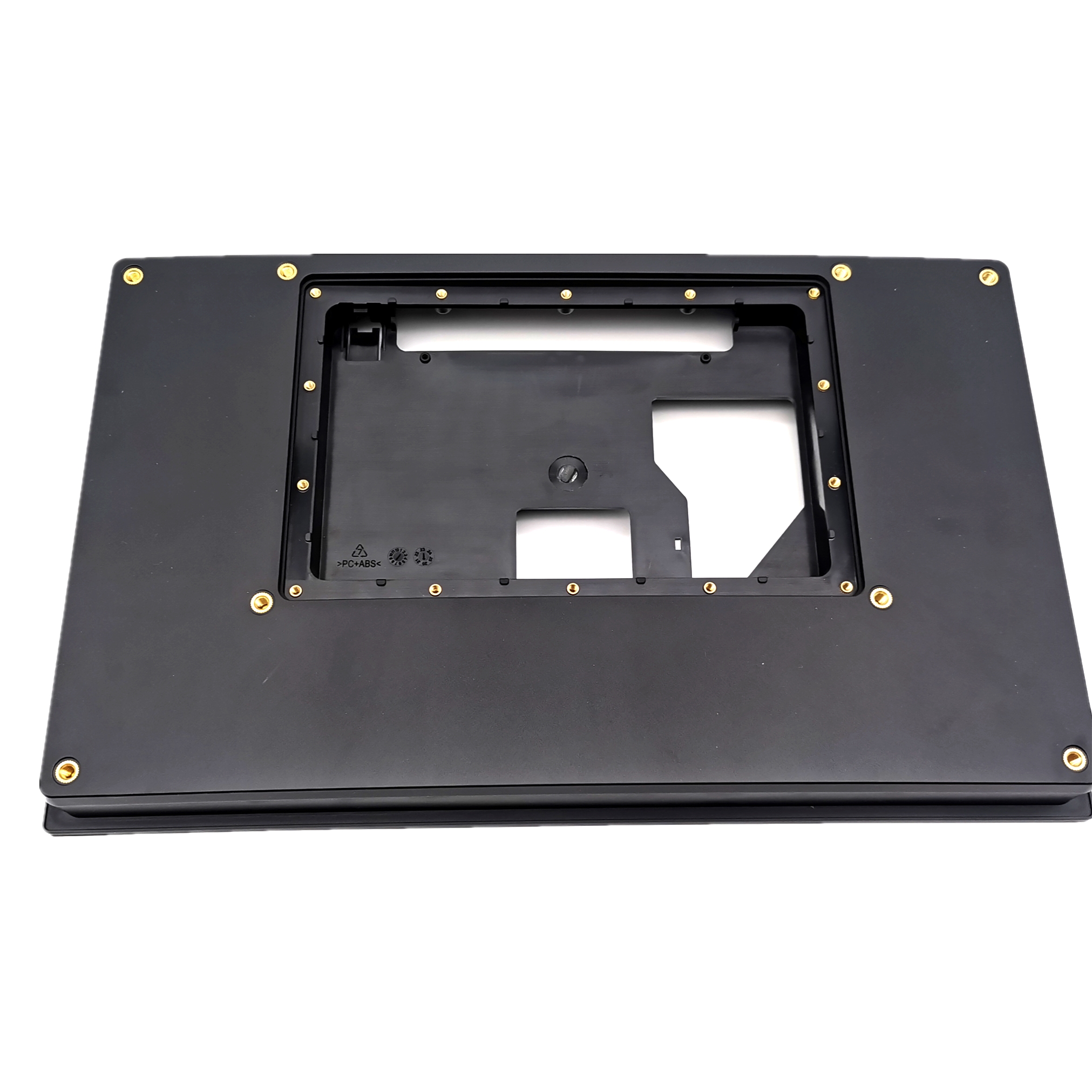


What Is Heat Riveting?
Heat riveting uses the same principle—localized heating and deformation of plastic—to secure metal parts. Instead of embedding a metal insert, a plastic stud or boss is melted and reshaped to act as a rivet head, clamping the metal part in place. This method typically forms a permanent joint.
Typical Process Steps:
- Plastic Stud Design: Plastic posts are designed with sufficient height and diameter for deformation.
- Part Placement: The metal part is placed over the plastic studs.
- Heating & Deformation: Heat and pressure soften and reshape the plastic to form a rivet head.
- Cooling: The newly formed plastic head cools and hardens, fixing the metal part securely.
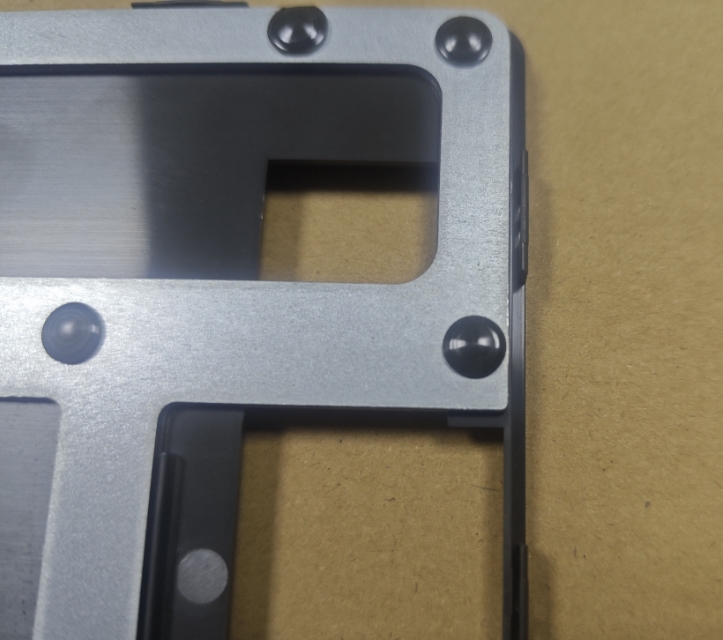

Advantages of Heat Riveting:
- No need for extra fasteners or adhesives
- Gentle on delicate metal surfaces
- Fast, clean, and suitable for automation
- Produces durable, long-term fastening
Comparison: Heat Staking vs. Heat Riveting
| Feature | Heat Staking | Heat Riveting |
|---|---|---|
| Type of Joint | Threaded insert in plastic | Plastic deformation for clamping |
| Disassemblable | Yes – supports repeated assembly | No – typically permanent |
| Extra Materials | Requires metal inserts | No additional fasteners needed |
| Automation Ready | Ideal for automated production | Also suitable for automation |
| Common Applications | Electronics, automotive, appliance housings | Brackets, panels, metal sheet assembly |
结论
From design consultation, mold making, plastic injection molding, to heat staking machine selection and automated assembly, we provide end-to-end solutions to our clients. With rich experience and strict quality control, we ensure every insert is precisely placed and firmly secured—enabling high-efficiency mass production.
Contact us today to explore a customized solution for your plastic-metal assembly needs.


