In the world of plastic injection molding, the mold—also known as a tool or die—is the core of the entire process. It acts as a precision “negative” of the final part, directly determining the product’s shape, dimensions, and quality. This article explores what an injection mold is and the critical steps involved in its manufacturing.
What is an Injection Mold?
An injection mold is a precision tool used to shape molten plastic into a specific form. Typically constructed from high-strength steel or aluminum, it contains a cavity that is the inverse of the final part’s geometry. During injection, molten plastic is forced under high pressure into this cavity. After cooling and solidifying, an ejection system releases the finished plastic part.
A high-quality mold is the foundation for ensuring manufacturing efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and part consistency.
(Figure 2: A detailed diagram or photo illustrating the key components of an injection mold.)
Image Box Title
Change this description
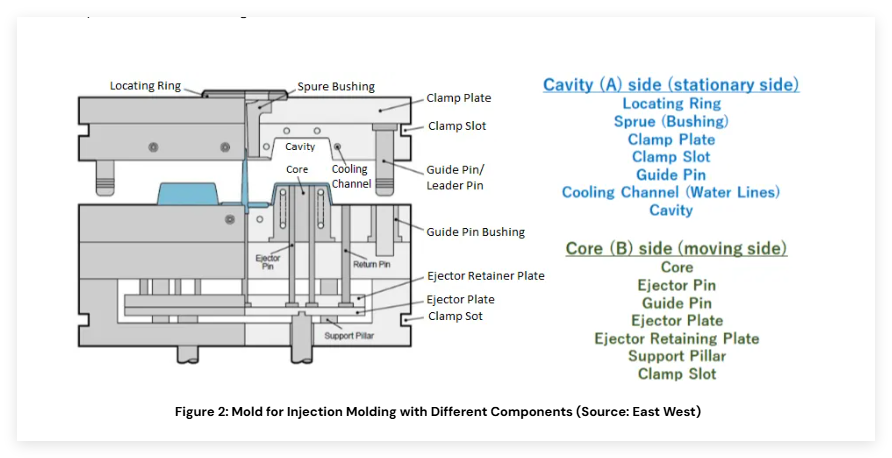
How is a Mold Manufactured?
Mold manufacturing is a collaborative process that integrates engineering design, precision machining, and close partnership between the mold maker and the customer. This ensures the final tool meets all specific requirements for design, fabrication, and production performance.
Phase 1: Collaborative Design & Engineering
The process begins with Computer-Aided Design (CAD), where engineers create detailed 2D and 3D models of the mold based on the customer’s part specifications. This critical phase involves optimizing the design for:
- Part Geometry: Ensuring the mold accurately replicates the product design.
- Material Characteristics: Accounting for the plastic’s shrinkage, flow behavior, and other properties.
- Cooling Requirements: Designing an efficient cooling channel layout to minimize cycle time and prevent defects.
- Ejection Mechanism: Planning how to eject the part smoothly and without damage.
- Mold Lifespan: Selecting appropriate materials and heat treatments to withstand the required production volume.
Image Box Title
Change this description

Phase 2: Precision Fabrication
Once the design is finalized, the mold maker begins the fabrication process. This involves high-precision machining techniques such as CNC milling, electrical discharge machining (EDM), and grinding. A key objective during this phase is to refine the mold’s structure to prevent potential production issues like air traps, warpage, and other part defects.
Phase 3: Lifespan Maintenance & Care
As a valuable asset, a mold’s operational life is extended through a rigorous maintenance regimen. Regular cleaning, lubrication, and inspection are essential to prevent premature wear and damage, ensuring long-term production stability and protecting your investment.
Image Box Title
Change this description




