Nano Injection Molding: Common in Mobile Phones and Computer Housings, but What Exactly Is It?
1. Combining Metal and Elastomers
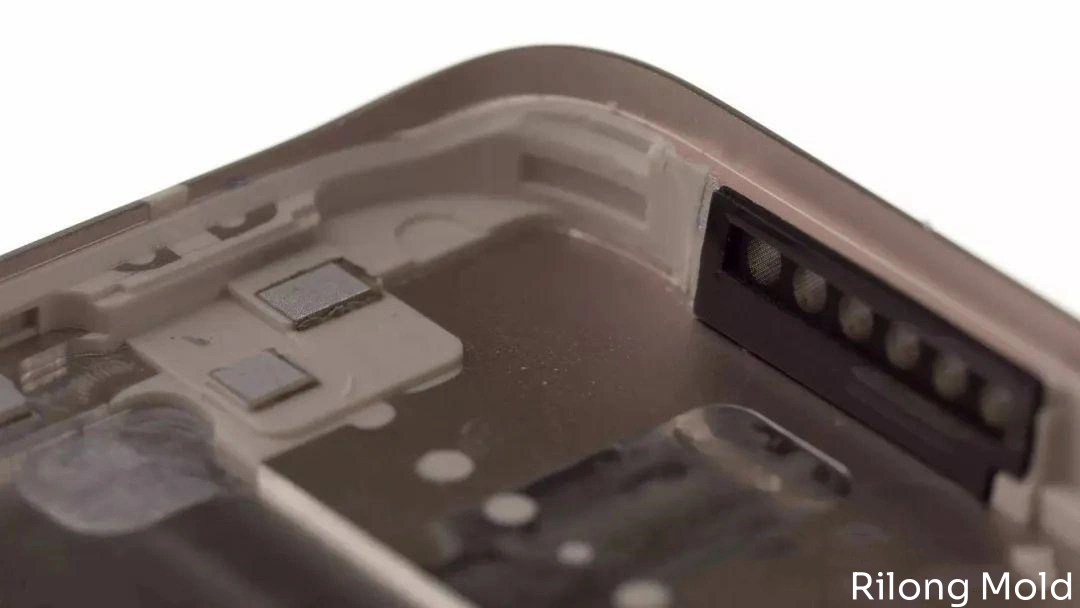

In this process, a special coating is applied to the metal surface, partially curing it before placing it in a mold. Thermoplastic elastomer (TPE) is then injected to form a unified structure with the metal.
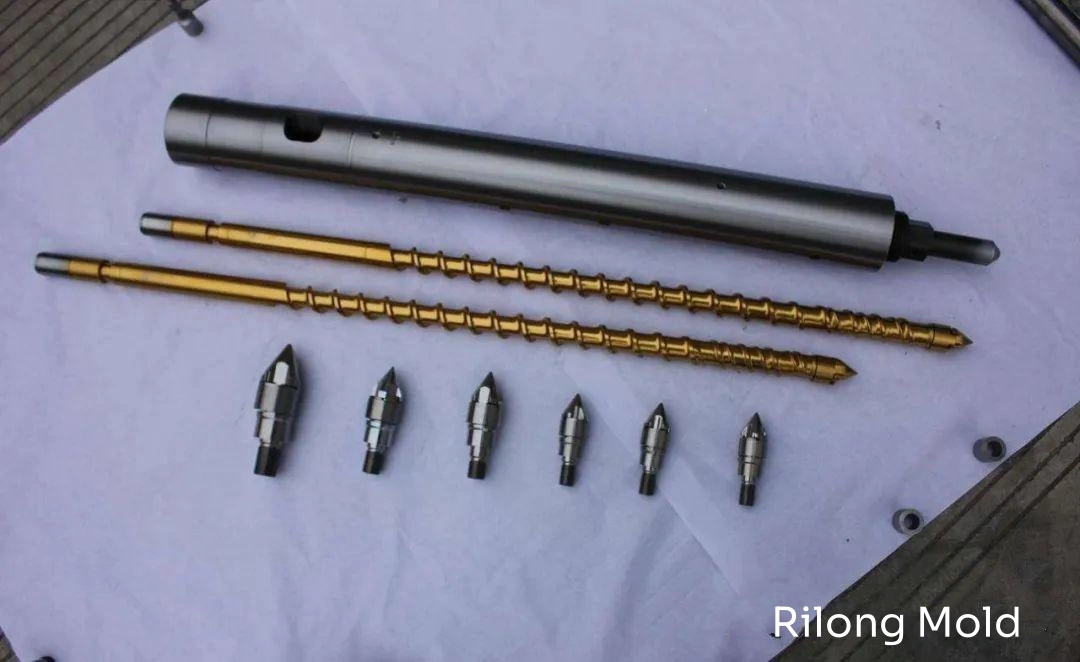

2. Combining Rigid Plastics and Metals
Now, nano injection molding can bond various metals, including aluminum, magnesium, copper, stainless steel, titanium, iron, and brass. Usable resins include PBT, PPS (like FORTRON®), Nylon-6, and Nylon-66. Since metals and resins have different linear thermal expansion coefficients, glass fibers and fillers are added to the resin to match the thermal expansion of the plastic to that of the metal, preventing peeling or damage at the bonding interface. This bond is neither adhesive nor chemical, but a physical fusion. The barrels of nano injection molding machines are slightly smaller and more precise than those of conventional machines.

3. Future Prospects of Nano Injection Molding
What are the advantages of nano injection molding? NMT (Nano Molding Technology) simplifies and shortens the manufacturing process, reduces unnecessary surface treatments by bonding materials like magnesium alloy without adhesives, and, being recyclable and safe, it has minimal environmental impact. Due to these advantages, nano injection molding is becoming a popular choice in manufacturing. Industry leaders like Foxconn, BYD, and Rilong Mold are investing heavily in NMT research, underscoring its significance.
How are Engineering Plastics Bonded to Metals?
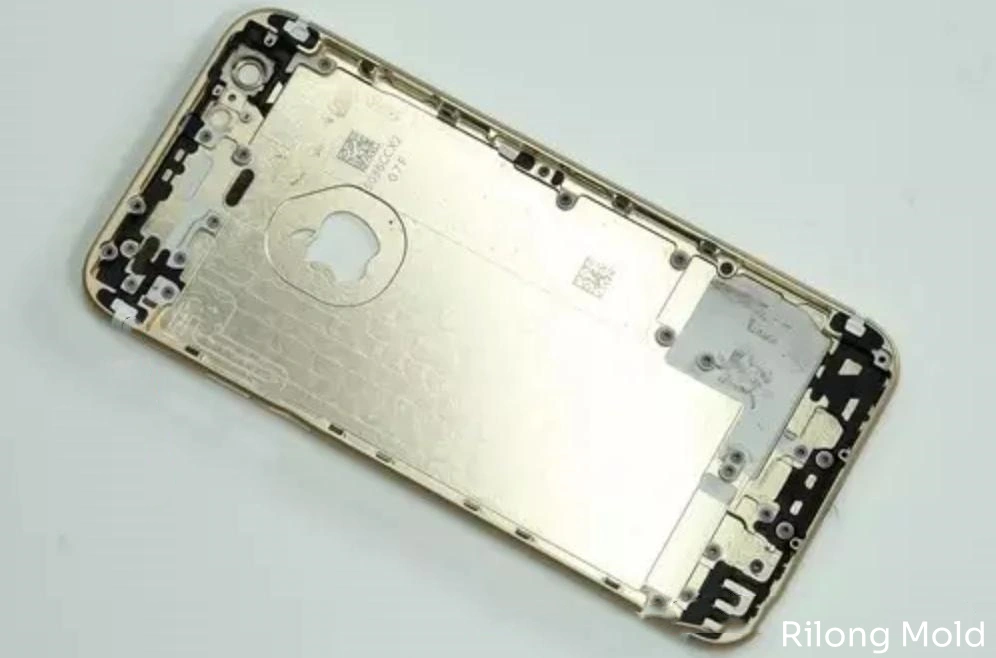
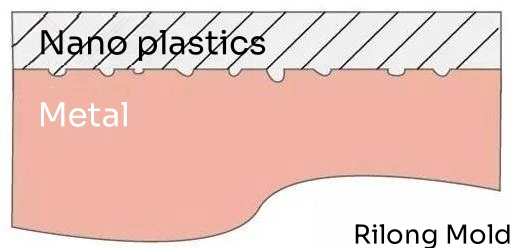
After nano-processing the metal surface, nano plastic is injected into the treated aluminum alloy, filling micro-pits in the alloy and forming a tightly integrated structure with high bonding strength and even resistance to liquid and gas penetration.
With the electron microscope, the processed metal surface not only retains a metallic aesthetic but also simplifies product design, making items lighter, thinner, shorter, and smaller. Compared to CNC processing, it offers better cost efficiency.